Vespel® SCP-5050 Saves Weight and Extends Shroud Life
Case StudyJet engine shrouds made with high-temperature resistant Vespel® SCP-5050 composite material offer proven impact resistance and potentially significant weight savings (40% less versus aluminum; 75% less versus stainless steel and titanium). Shrouds made with Vespel® SCP-5050 also provide longer component life thanks to reduced wear interfaces, utilization of bearing material for the entire shroud, and elimination of bushing life issues.
Composite shrouds provide a low-friction, wear-resistant surface that prevents damage to expensive metal vane stems. Further, Vespel® SCP-5050 can simplify design and assembly, and the weight savings realized by using this material can help improve aircraft fuel efficiency, range and payload capacity.
Application
- A shroud is a segmented ring with holes drilled radially outward for variable vane stems used inside a jet engine compressor. Some are split.
- Grooves are cut into shroud to accept metal connecting ring, frequently with an abradable seal.
- Shrouds are typically aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium.
- Shrouds utilize bushings to enhance wear and reduce friction for variable vane stems.
- Inner shrouds typically float on the engine axis.
Challenges
- Damage can occur to expensive metal components such as vanes if bushings wear out prematurely.
- Components need to withstand thermal excursions for duration of expected engine life.
- Shrouds need to withstand impact, loading, and maintain relative location of vanes.
- Shrouds need to be designed to allow simultaneous assembly with multiple vanes.
More Hot Wear Resistance
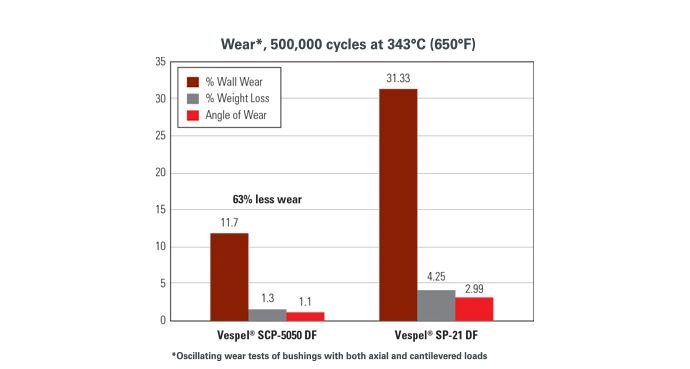
Solution
Design shrouds in light weight, high temperature, wear resistant Vespel® SCP-5050 composite material instead of metal.
Features and Benefits
- High temperature material capabilities in application environments in excess of 600°F/315°C.*
- Longer component life due to reduced wear interfaces, utilization of bearing material for entire shroud, and elimination of bushing life issues.
- Proven impact resistance.
- Potential weight savings of 40% over aluminum and 75% over stainless steel and titanium due to lower density of composite materials.
- Fewer parts to stock and assemble through bushing elimination.
- Lower system cost through part consolidation.
- Provide largest subassembly possible.
- Lower friction vs. metal with dynamic coefficient of .2 or less.
- Vibration dampening properties of composites versus metals.
Stiff when Hot
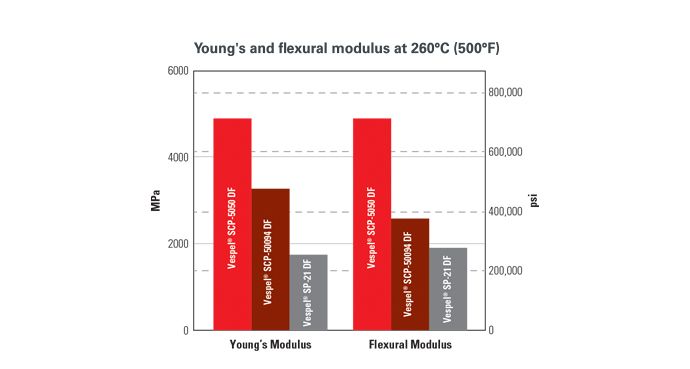
Ideas & innovations
Powered by a broad product portfolio and state-of-the-art expertise, we help our partners meet the critical industry demands of the electrical and electronics market.
Featured resources
Literature
DuPont™ Vespel® CP Grades as Lightweight Performance Clamps
DuPont Vespel ASB-0664 Thrust Reversers - Application Profile
Case Studies
Vespel® CP-0664 Enhances Fan Blade Performance and Durability
Articles


