Line Shaft Bearings for Pumps
Case Study
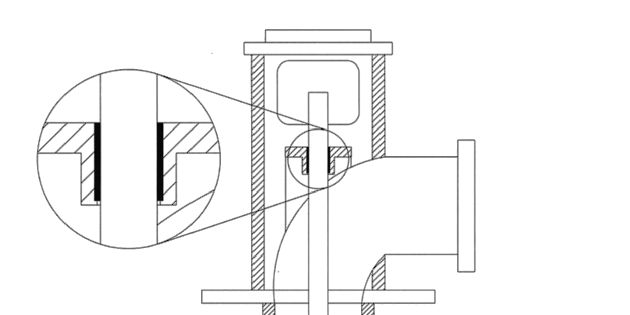
When Hot Well Pumps Run Dry, Vespel® CR-6100 parts for line shaft bearings
The Challenge
About three times a year, run-dry conditions were causing failure of line shaft bearings or stationary wear rings in two vertical pumps for hot condensate (water) at a major oil refinery. Seizure was the most common failure mode. Process temperature is 180°F (82°C).
Several thermoplastics were tried but failed because their high coefficient of thermal expansion caused the line shaft bearings to "grow into" the shaft. The parts were destroyed when the pump ran dry.
The Solution
Retrofitting the pumps with DuPont™ Vespel® CR-6100 parts for line shaft bearings and stationary wear rings.
To demonstrate that Vespel® CR-6100 parts could survive these conditions, site personnel installed a retrofitted pump and performed a field test. The suction valve was closed and amps were monitored to verify that the pump was not seizing. After 30 minutes with suction pressure showing 18 inches of vacuum, the ammeter reading did not change, indicating there was no damage.
Key Advantages
In over four years of service, no seizure failures have been reported by the refinery. This contrasts sharply with the previous pattern of three seizure failures per year.
Due to its success in the condensate return pumps and subsequent applications at the refinery, Vespel® CR-6100 has become a standard material for wear rings and line shaft bearings. It has been successfully applied to hundreds of the refinery’s pumps.
One refinery’s experience after 68 months cumulative population run time after conversions from metal wear parts to Vespel® CR-6100 pump components improved by almost 50 percent.
DuPont™ Vespel® CR-6100 was selected for the line shaft bearings and stationary wear rings because it was demonstrated that it could survive when the pump ran dry. Site personnel also wanted a material that could run with reduced clearances and could survive in the process for extended periods of time. The material’s low coefficient of thermal expansion, low coefficient of friction, high PV capacity, low wear rate, and low water absorption were crucial to its success in these applications.
Ideas & innovations
Powered by a broad product portfolio and state-of-the-art expertise, we help our partners meet the critical industry demands of the electrical and electronics market.
Featured resources
Literature
Vespel® CR-6100 Compression Molded Parts and Shapes
Vespel® CR-6100 Bearings for API Separators
Vespel® CR-6100 Pipeline Pump Component Boost Efficiency
Case Studies
Articles
Additional links